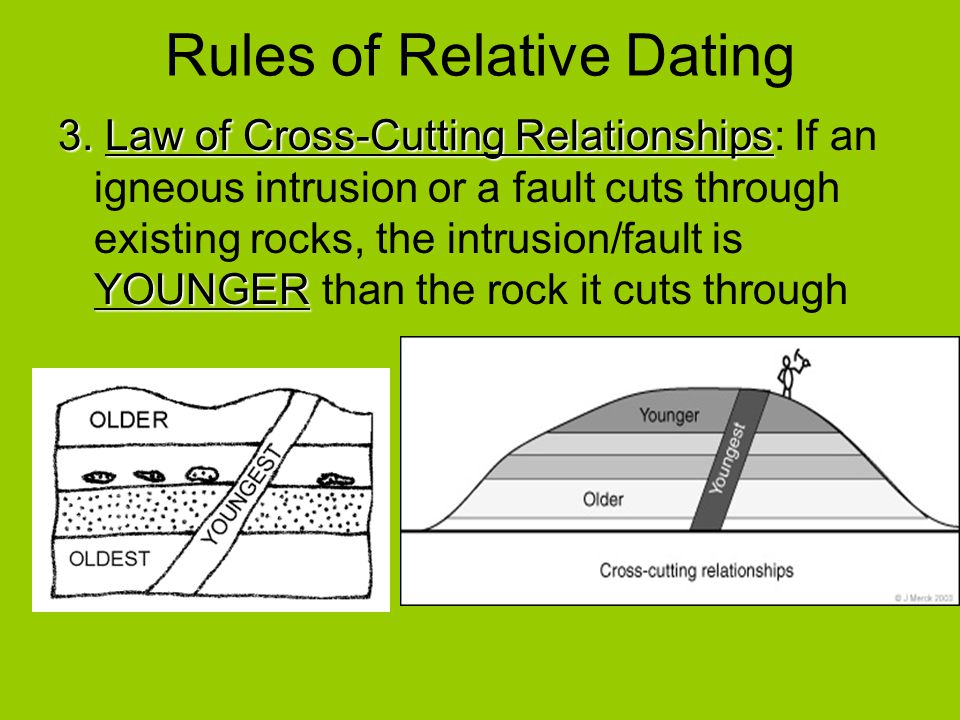
There are two types of intrusions: Intrusive - molten rocks that cuts through the pre existing rocks. When a observer or geologist come across sedimentary layers with an intrusion, the intrusion is the youngest event to have occurred.
Relative dating - Wikipedia
The dashed lines indicate contact metamorphism. Remember, contact metamorphism is changes in a rock due to contact with magma or lava. Think of it as a boundary layer between igneous rocks and sedimentary rocks. Faults - breaks in the rock where movements has occurred. Fossils - are the preserved remains or traces of living things that lived millions of years ago.
Fossils can help geologists determine the age of geologic strata.
For example, if you have one type of organism that lived 10 million years ago and it is found within one geologic layer, then you have a better clue of the age of that layer. Such fossils are called Index Fossils. Index fossils - Organisms that have lasted a very short period of geologic time but found over large portions of Earth.
Index fossils are also used to correlate or match up geologic layers. In June, it is almost a certainty that you will have to answer questions that asks you the order of geologic events. The geologic formation that you may see will be complicated as the illustrations below. Now you must become a geologists an try to place the geologic events in proper order. But there are several details that you must know before you can place these events in order. Sometimes, geologic layers are missing in sequence.
This is due to the erosion of the layers. Lastly the Principle of Fossil Succession.
- Navigation menu.
- black lady dating site.
- Geology Online Subchapter;
- virginia tech dating service.
Aside from single-celled bacteria, most living organism reside at or very near the Earth's surface either in continental or oceanic environments. As these organisms die they are deposited on the surface along with all other sediments.
If conditions are right the remains of the dying organisms can then be preserved as fossils within the rock that formed from sediments that covered the remains. Since, all sedimentary rock is formed through the gradual accumulation of sediment at the surface over time, and since the principle of superposition tells us that newer sediment is deposited on top of older sediment, the same must also be true for fossils contained within the sediment.
Although this principle is generally applied to relative dating it is also the basis for evolution. Principles of Relative The Principle of Superposition tells us that deeper layers of rock are older than shallower layers Relative dating utilizes six fundamental principles to determine the relative age of a formation or event. Image demonstrating a common use of the principle of lateral continuity Principle of Cross-Cutting tells us that the light colored granite must be older than the darker basalt dike intruding the granite.
This is a restatement of Charles Lyell 's original principle of inclusions and components from his to multi-volume Principles of Geology , which states that, with sedimentary rocks , if inclusions or clasts are found in a formation , then the inclusions must be older than the formation that contains them. These foreign bodies are picked up as magma or lava flows , and are incorporated, later to cool in the matrix.
As a result, xenoliths are older than the rock which contains them Relative dating is used to determine the order of events on Solar System objects other than Earth; for decades, planetary scientists have used it to decipher the development of bodies in the Solar System , particularly in the vast majority of cases for which we have no surface samples. Many of the same principles are applied. For example, if a valley is formed inside an impact crater , the valley must be younger than the crater. Craters are very useful in relative dating; as a general rule, the younger a planetary surface is, the fewer craters it has.
If long-term cratering rates are known to enough precision, crude absolute dates can be applied based on craters alone; however, cratering rates outside the Earth-Moon system are poorly known. Relative dating methods in archaeology are similar to some of those applied in geology. The principles of typology can be compared to the biostratigraphic approach in geology. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
The Grand Canyon and Relative Dating
For relative dating of words and sounds in languages, see Historical linguistics. Dating methodologies in archaeology. EJ Brill , The earth through time 9th ed.
- You must create an account to continue watching?
- Chapter 5-Intepreting Earths History.
- vancouver free online dating site;
- Relative Age Determination!
Dinosaurs and the History of Life. HarperCollins, , pp. Canon of Kings Lists of kings Limmu. Chinese Japanese Korean Vietnamese. Lunisolar Solar Lunar Astronomical year numbering. Deep time Geological history of Earth Geological time units.
Relative dating
Chronostratigraphy Geochronology Isotope geochemistry Law of superposition Luminescence dating Samarium—neodymium dating. Amino acid racemisation Archaeomagnetic dating Dendrochronology Ice core Incremental dating Lichenometry Paleomagnetism Radiometric dating Radiocarbon Uranium—lead Potassium—argon Tephrochronology Luminescence dating Thermoluminescence dating.
Fluorine absorption Nitrogen dating Obsidian hydration Seriation Stratigraphy. Retrieved from " https: Biostratigraphy Dating methods Geochronology. Webarchive template wayback links.
Teacher Resources
Views Read Edit View history. This page was last edited on 27 December , at By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Concepts Deep time Geological history of Earth Geological time units.