- Radiocarbon dating
- Presentation on theme: "A Study of the Doctrine of Creation"— Presentation transcript:
- Absolute dating - Wikipedia
During sediment transport, exposure to sunlight 'zeros' the luminescence signal. Upon burial, the sediment accumulates a luminescence signal as natural ambient radiation gradually ionises the mineral grains. Careful sampling under dark conditions allows the sediment to be exposed to artificial light in the laboratory which releases the OSL signal. The amount of luminescence released is used to calculate the equivalent dose De that the sediment has acquired since deposition, which can be used in combination with the dose rate Dr to calculate the age.
Dendrochronology or tree-ring dating is the scientific method of dating based on the analysis of patterns of tree rings , also known as growth rings. Dendrochronology can date the time at which tree rings were formed, in many types of wood, to the exact calendar year. Dendrochronology has three main areas of application: In some areas of the world, it is possible to date wood back a few thousand years, or even many thousands. Currently, the maximum for fully anchored chronologies is a little over 11, years from present.
Radiocarbon dating
Amino acid dating is a dating technique [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] used to estimate the age of a specimen in paleobiology , archaeology , forensic science , taphonomy , sedimentary geology and other fields. This technique relates changes in amino acid molecules to the time elapsed since they were formed.
All biological tissues contain amino acids. All amino acids except glycine the simplest one are optically active , having an asymmetric carbon atom. This means that the amino acid can have two different configurations, "D" or "L" which are mirror images of each other. With a few important exceptions, living organisms keep all their amino acids in the "L" configuration. When an organism dies, control over the configuration of the amino acids ceases, and the ratio of D to L moves from a value near 0 towards an equilibrium value near 1, a process called racemization.
Thus, measuring the ratio of D to L in a sample enables one to estimate how long ago the specimen died.
- Geological Time - Doral Academy Preparatory.
- 14L final -revised 02-13 Geological Time.
- hook up seafood baton rouge menu.
- hook up lights to speakers!
- adam4adam gay dating site.
- no fee online dating sites.
- A Radiometric Dating Resource List.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. This section does not cite any sources.
Presentation on theme: "A Study of the Doctrine of Creation"— Presentation transcript:
Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
July Learn how and when to remove this template message. Archaeology of ancient Mexico and Central America: Down to Earth Fifth edition. American Journal of Archaeology. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences. International Journal of Chemical Kinetics. The results provide a compelling case for applicability of amino acid racemization methods as a tool for evaluating changes in depositional dynamics, sedimentation rates, time-averaging, temporal resolution of the fossil record, and taphonomic overprints across sequence stratigraphic cycles. Chronometric dating in archaeology, edited by R.
Taylor and Martin J. Plenum Press in cooperation with the Society for Archaeological Sciences. Canon of Kings Lists of kings Limmu. Chinese Japanese Korean Vietnamese. Lunisolar Solar Lunar Astronomical year numbering. Deep time Geological history of Earth Geological time units. Chronostratigraphy Geochronology Isotope geochemistry Law of superposition Luminescence dating Samarium—neodymium dating. Amino acid racemisation Archaeomagnetic dating Dendrochronology Ice core Incremental dating Lichenometry Paleomagnetism Radiometric dating Radiocarbon Uranium—lead Potassium—argon Tephrochronology Luminescence dating Thermoluminescence dating.
Absolute dating - Wikipedia
Fluorine absorption Nitrogen dating Obsidian hydration Seriation Stratigraphy. Retrieved from " https: Articles needing additional references from July All articles needing additional references. Views Read Edit View history. This page was last edited on 16 January , at By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. The Wikibook Historical Geology has a page on the topic of: Finally periods are divided into still smaller units called epochs. Below is the Geological Time Scale.
This is because Precambrian time, there were fewer life forms. These life forms are more difficult to identify and the rocks have been disturbed often. In geology the principal laws are: In the above picture a vertical column of magma called a dike cooled into igneous rock. The magma that cooled into igneous rock that cut across the other three layers of rock is younger than the three other layers.
Ignore letters D and I. Rock layers from the oldest to the youngest: Rock layer D represents a pocket of magma that traveled up from beneath layers A and B which hardened into igneous rock. Order the rock layers in order from the oldest to youngest. Is a place where rock layers are missing. After, the process of weathering and erosion can wear the rock layer away.
Rock layers often occur above the unconformity, but they are not the kind of rock that would have formed in the same way as the rock layer beneath the unconformity. Is a way to describe the age of one event compared to another object or event. Relative age dating is based on comparisons of the age of objects. Thus, this method of dating objects always includes words such as before, after, earlier, later, older, and younger.
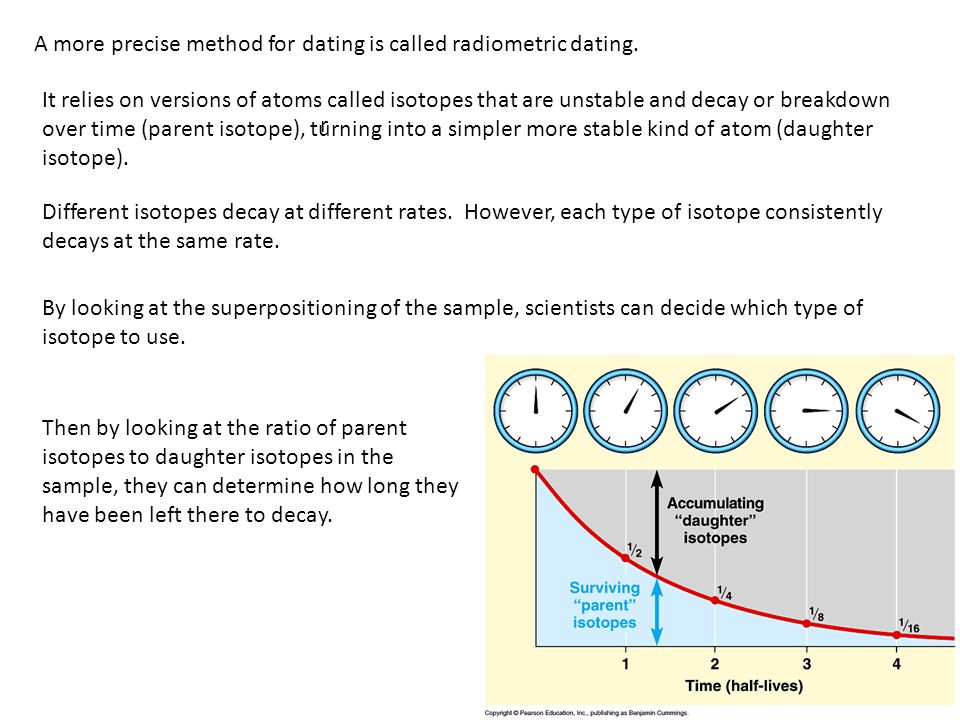
Example using the principal of superposition: If you found an arrow head in one sedimentary layer of rock and a saber tooth tiger skull in a lower layer of rock, you can use the law of superposition to conclude that the skull is older than the arrow head. This describes the actual age of an object or event. The absolute ages of objects from long ago are found by analyzing the chemicals in the object or the rock layers in which they were found. Radiometric Dating — This is the most accurate form of dating.
Carbon Dating The 14 is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of the atom Most atoms of carbon have 6 protons and 6 neutrons in the nucleus of atom. A very few carbon atoms have a different number of neutrons and are called isotopes. In conclusion, an isotope is an atom of the same element with a different amount of neutrons in the nucleus.
Carbon is an isotope of carbon and is radioactive. Radioactive describes an element that gives off tiny particles and energy from inside its atom.
